What is Albedo?
Albedo is a non-dimensional, unitless quantity that indicates how well a surface reflects solar energy.
- Albedo is the portion of solar energy reflected from the surface of the Earth back into space. It is a reflection coefficient and has a value of less than one.
- When the solar radiation passes through the atmosphere, a certain amount of it is scattered, reflected and absorbed. The reflected sum of radiation is called the albedo of the earth.
- Albedo is an important concept in climatology, astronomy, and environmental management.
- It plays a major role in the energy balance of the earth’s surface, as it defines the rate of the absorbed portion of the incident solar radiation
- Albedo varies between 0 and 1.
- Albedo commonly refers to the “whiteness” of a surface, with 0 meaning black and 1 meaning white.
- A value of 0 means the surface is a “perfect absorber” that absorbs all incoming energy.
- Absorbed solar energy can be used to heat the surface or, when sea ice is present, melt the surface.
- A value of 1 means the surface is a “perfect reflector” that reflects all incoming energy.
Values of Albedo
- Different surfaces have different values.
- Albedo is higher in Snow or Ice.
- All black surfaces have the lowest albedo.
- Albedo : Fresh Snow > Old Snow > Thick Cloud > Thin Cloud > Sea Ice > Glacier > Dry Sand > Dry Soil > Grass > Crops.
| Surface | Albedo |
| Dark and Wet Soil | 0.05 |
| Light and Dry Soil | 0.40 |
| Sand | 0.15-0.45 |
| Long Grass | 0.16 |
| Short Grass | 0.26 |
| Agricultural Crops | 0.18-0.25 |
| Tundra | 0.18-0.25 |
| Deciduous Forest | 0.15-0.20 |
| Coniferous Forest | 0.05-0.15 |
| Water (Small Zenith Angle) | 0.03-0.10 |
| Water (Large Zenith Angle) | 0.10-1.00 |
| Snow (Old) | 0.40 |
| Snow (Fresh) | 0.95 |
| Ice (Sea) | 0.30-0.45 |
| Ice (Glacier) | 0.20-0.40 |
| Clouds (Thick) | 0.60-0.90 |
| Clouds (Thin) | 0.30-0.50 |
- Albedo generally applies to visible light, although it may involve some of the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Sea ice has a much higher albedo compared to other Earth surfaces, such as the surrounding ocean. A typical ocean albedo is approximately 0.06, while bare sea ice varies from approximately 0.5 to 0.7. This means that the ocean reflects only 6 percent of the incoming solar radiation and absorbs the rest, while sea ice reflects 50 to 70 percent of the incoming energy. The sea ice absorbs less solar energy and keeps the surface cooler.
- Snow has an even higher albedo than sea ice, and so thick sea ice covered with snow reflects as much as 90 percent of the incoming solar radiation. This serves to insulate the sea ice, maintaining cold temperatures and delaying ice melt in the summer. After the snow does begin to melt, and because shallow melt ponds have an albedo of approximately 0.4 to 0.5, the surface albedo drops to about 0.75. Albedo drops further as melt ponds grow and deepen.
Types of Albedo
There are two types of Albedo:
Terrestrial Albedo
The amount reflected back out to space is called the planetary albedo. It’s calculated by averaging the albedo of all Earth surfaces – including the land, ocean, and ice. Above the Earth surface, clouds reflect large amount of sunlight out to space too. Earth’s planetary albedo is about 31% meaning that about a third of the solar energy that gets to Earth is reflected out to space.
- The measurement of Earth’s albedo is known as Terrestrial Albedo.
- The Terrestrial Albedo of Earth around 0.31 which is about two-thirds of the solar radiation reaching the Earth.
- This figure is dependent on many factors like an ocean, forest, clouds, deserts etc.
Astronomical Albedo
- Astronomical albedo is the measure of the reflectivity of planets (excluding Earth), asteroids and other celestial bodies the albedo is an indicator of the surface and atmospheric characteristics of a celestial body.
- It is important in the study of astronomy.
- The difference in the average albedo of Earth has an important influence on the temperature of the Earth.
- If the average albedo is lower than the previous year’s albedo, it specifies that the amount of radiation absorbed is higher
- This results in the rise in the temperature of the Earth.
- Earth’s albedo is constantly measured using satellites to monitor global warming.
ALBEDO Effect
Albedo effect has a significant impact on our climate. The lower the albedo, the more radiation from the Sun that gets absorbed by the planet, and temperatures will rise. If the albedo is higher, and the Earth is more reflective, more of the radiation is returned to space, and the planet cools.
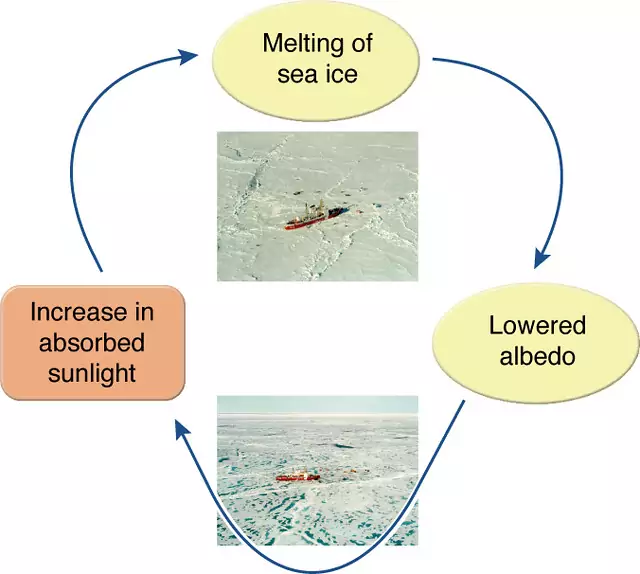
An example of this albedo effect is the snow temperature feedback. When you have a snow covered area, it reflects a lot of radiation. This is why you can get terrible sunburns when you’re skiing. But then when the snow covered area warms and melts, the albedo goes down. More sunlight is absorbed in the area and the temperatures increase. Climate scientists are concerned that global warming will cause the polar ice caps to melt. With these melting caps, dark ocean water will absorb more sunlight, and contribute even more to global warming.
How does the Albedo of Earth affect Climate?
If Earth’s climate is colder and there is more snow and ice on the planet, albedo increases, more sunlight is reflected out to space, and the climate gets even cooler. But, when warming causes snow and ice to melt, darker colored surfaces are exposed, albedo decreases, less solar energy is reflected out to space, and the planet warms even more. This is known as the ice-albedo feedback.
Albedo and Global Warming
- The difference in the average albedo of Earth has an important influence on the temperature of the Earth.
- If the average albedo is lower than the previous year’s albedo, it specifies that the amount of radiation absorbed is higher
- This results in the rise in the temperature of the Earth.
- Earth’s albedo is constantly measured using satellites to monitor global warming.
- Earth observation satellites are constantly measuring the Earth’s albedo using a suite of sensors, and the reflectivity of the planet can actually be measured through Earthshine – light from the Earth that reflects off the Moon.
- Different parts of the Earth contribute to our planet’s overall albedo in different amounts. Trees are dark and have a low albedo, so removing trees might actually increase the albedo of an area; especially regions typically covered in snow during the winter.
- Clouds can reflect sunlight, but they can also trap heat warming up the planet. At any time, about half the Earth is covered by clouds so their effect is significant.
Frequently asked Questions about Albedo
What is Albedo?
Albedo is a non-dimensional, unitless quantity that indicates how well a surface reflects solar energy. Albedo varies between 0 and 1. Albedo commonly refers to the “whiteness” of a surface, with 0 meaning black and 1 meaning white.
Why is Albedo important?
Albedo is the reflectivity of a surface. A surface that has a high albedo reflects a lot of solar radiation from the sun back into the atmosphere, whilst a surface that has a low albedo reflects little solar radiation, absorbing it instead.
Which surface of Earth has the lowest albedo?
All black surfaces have the lowest albedo. Dark and Wet Soil have the Albedo of 0.05.
Which has the highest and which has the lowest albedo value?
Fresh snow has the largest reflection and hence highest albedo, whereas black soil has the lowest albedo since it absorbs maximum amount of solar radiation.
Also refer: