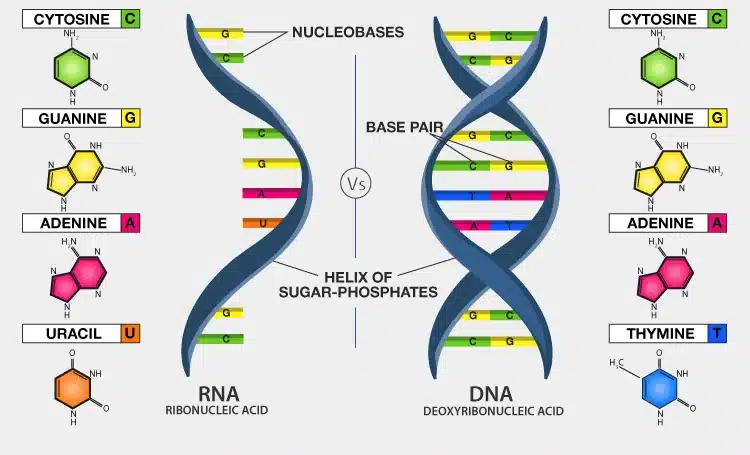
Following are the important differences between DNA and RNA:
| DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) | RNA (Ribonucleic acid) |
| DNA replicates and stores genetic information. It is a blueprint for all genetic information contained within an organism | RNA converts the genetic information contained within DNA to a format used to build proteins, and then moves it to ribosomal protein factories. |
| It is a long polymer. It has a deoxyribose and phosphate backbone having four distinct bases: thymine, adenine, cytosine and guanine. | It is a polymer with a ribose and phosphate backbone with four varying bases: uracil, cytosine, adenine and guanine. |
| DNA consists of two strands, arranged in a double helix. These strands are made up of subunits called nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate, a 5-carbon sugar molecule and a nitrogenous base. | RNA only has one strand, but like DNA, is made up of nucleotides. RNA strands are shorter than DNA strands. RNA sometimes forms a secondary double helix structure, but only intermittently. |
| It is located in the nucleus of a cell and in the mitochondria. | It is found in the cytoplasm, nucleus and in the ribosome. |
| The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, which contains one less hydroxyl group than RNA’s ribose. | RNA contains ribose sugar molecules, without the hydroxyl modifications of deoxyribose. |
| DNA replicates on its own, it is self-replicating. | RNA does not replicate on its own. It is synthesized from DNA when required. |
| The base pairing is as follows: G-C (Guanine pairs with Cytosine) A-T (Adenine pairs with Thymine). | The base pairing is as follows: G-C (Guanine pairs with Cytosine) A-U (Adenine pairs with Uracil). |
| DNA is vulnerable to damage by ultraviolet light. | RNA is more resistant to damage from UV light than DNA. |
| Due to its deoxyribose sugar, which contains one less oxygen-containing hydroxyl group, DNA is a more stable molecule than RNA, which is useful for a molecule which has the task of keeping genetic information safe. | RNA, containing a ribose sugar, is more reactive than DNA and is not stable in alkaline conditions. RNA’s larger helical grooves mean it is more easily subject to attack by enzymes. |
DNA
- In cells, DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the nucleic acid that functions as the original blueprint for the synthesis of proteins.
- It is made up of nucleotides which contain nitrogenous group, a phosphate group, and a sugar group.
- The order of the nitrogenous bases – thymine(T), guanine(G), cytosine(C), and adenine(A), is crucial in determining the genetic code.
- The bases located on one strand pair up with the bases on the other strand, as in – guanine pairs with cytosine and adenine pairs with thymine.
- The DNA molecules contain instructions a living entity requires to grow, develop and reproduce.
- These instructions are present inside each cell and are inherited from the parents to their offsprings.
- The DNA molecules are extremely long and hence without the right packaging, they cannot fit into cells. Thus, DNA is tightly coiled to produce formations referred to as chromosomes. Every chromosome has a single DNA molecule. In humans, there are 23 pairs of chromosomes that are present within the nucleus of the cells.
RNA
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a nucleic acid which is directly involved in protein synthesis.
- Ribonucleic acid is an important nucleotide with long chains of nucleic acid present in all living cells.
- Its main role is to act as a messenger conveying instructions from DNA for controlling the proteins synthesis.
- RNA contains the sugar ribose, phosphates, and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and uracil (U).
- DNA and RNA share the nitrogenous bases A, G, and C.
- Thymine is usually only present in DNA and uracil is usually only present in RNA.
Types Of RNA
Only some of the genes in cells are expressed into RNA. The following are the types of RNA wherein each type is encoded by its own type of gene:
- tRNA– The transfer RNA or the tRNA carries amino acids to ribosomes while translation
- mRNA – The messenger RNA or the mRNA encodes amino acid sequences of a polypeptide
- rRNA – The ribosomal RNA or the rRNA produces ribosomes with the ribosomal proteins that are organelles responsible for the translation of the mRNA.
- snRNA – The small nuclear RNA forms the complexes along with proteins which are utilized in RNA processing in the eukaryotes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the composition of DNA and RNA?
DNA and RNA are nearly identical polymers of nucleotide, except for the base pairs. DNA contains thymine while the same is substituted with uracil in RNA.
Where are DNA and RNA found?
DNA is located in the nucleus of a cell and in the mitochondria. Meanwhile, RNA is found in the cytoplasm, nucleus, and also in the ribosomes.
How does propagation occur in DNA and RNA?
DNA is capable of self-replication but RNA cannot self-replicate and instead, it is synthesized from DNA (DNA transcription) when required.
What is the similarity between DNA and RNA?
Three out of the four nitrogenous bases in DNA and RNA are the same (cytosine, adenine, guanine). They both possess a phosphate backbone to which the bases attach.
Why is DNA a better genetic material than RNA?
The deoxyribose sugar of DNA contains one less oxygen-containing hydroxyl group. DNA is a more stable nucleic acid. RNA, on the other hand, contains a ribose sugar and is more reactive than DNA. Therefore, DNA is a better genetic material than RNA.
Also refer :