Difference Between Plant Cell And Animal Cell
All living things are made up of cells. Cells are the basic unit of a living organism and where all life processes are carried out.
Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic, so they contain membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria. However, plant cells and animal cells do not look exactly the same or have all of the same organelles, since they each have different needs. For example, plant cells contain chloroplasts since they need to perform photosynthesis, but animal cells do not.
Animal cells
Animals are made up of millions of cells. Animal cells have an irregular structure and are made up of four key parts:
- Nucleus – This contains genetic material (DNA), and controls the cell’s activity.
- Cell membrane – A flexible layer that surrounds the cell and controls the substances that enter and exit.
- Cytoplasm – A jelly-like substance where the chemical reactions happen.
- Mitochondria – This is where energy is released from the food molecules.
Plant cells
Plants are also made up of millions of cells. Plant cells have a nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm and mitochondria too, but they also contain the following structures:
- Cell wall – A hard layer outside the cell membrane, containing cellulose to provide strength to the plant.
- Vacuole – A space inside the cell that is used to store substances and help the cell keep its shape.
- Chloroplasts – Structures that contain the green pigment chlorophyll, which are a key part of photosynthesis.
Plant Cell and Animal Cell can be differentiated on the following parameters :
Size
Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells. Animal cells range from 10 to 30 micrometers in length, while plant cells range from 10 and 100 micrometers in length.
Shape
Animal cells come in various sizes and tend to have round or irregular shapes. Plant cells are more similar in size and are typically rectangular or cube shaped.
Energy Storage
Animals cells store energy in the form of the complex carbohydrate glycogen. Plant cells store energy as starch.
Proteins
Of the 20 amino acids needed to produce proteins, only 10 can be produced naturally in animal cells. The other so-called essential amino acids must be acquired through diet. Plants are capable of synthesizing all 20 amino acids.
Differentiation
In animal cells, only stem cells are capable of converting to other cell types. Most plant cell types are capable of differentiation.
Growth
Animal cells increase in size by increasing in cell numbers. Plant cells mainly increase cell size by becoming larger. They grow by absorbing more water into the central vacuole.
Cell Wall
Animal cells do not have a cell wall but have a cell membrane. Plant cells have a cell wall composed of cellulose as well as a cell membrane.
Centrioles
Animal cells contain these cylindrical structures that organize the assembly of microtubules during cell division. Plant cells do not typically contain centrioles.
Cilia
Cilia are found in animal cells but not usually in plant cells. Cilia are microtubules that aid in cellular locomotion.
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm during cell division, occurs in animal cells when a cleavage furrow forms that pinches the cell membrane in half. In plant cell cytokinesis, a cell plate is constructed that divides the cell.
Glyoxysomes
These structures are not found in animal cells but are present in plant cells. Glyoxysomes help to degrade lipids, particularly in germinating seeds, for the production of sugar.
Lysosomes
Animal cells possess lysosomes which contain enzymes that digest cellular macromolecules. Plant cells rarely contain lysosomes as the plant vacuole handles molecule degradation.
Plastids
Animal cells do not have plastids. Plant cells contain plastids such as chloroplasts, which are needed for photosynthesis.
Plasmodesmata
Animal cells do not have plasmodesmata. Plant cells have plasmodesmata, which are pores between plant cell walls that allow molecules and communication signals to pass between individual plant cells.
Vacuole
Animal cells may have many small vacuoles. Plant cells have a large central vacuole that can occupy up to 90% of the cell’s volume.
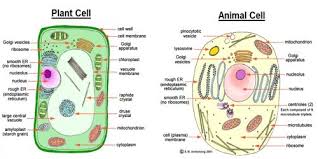
The major differences between the plant cell and animal cell are tabulated below:
| Parameter | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| Cell Shape | Square or rectangular in shape | Irregular or round in shape |
| Cell Wall | Present | Absent |
| Plasma/Cell Membrane | Present | Present |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Present | Present |
| Nucleus | Present and lies on one side of the cell | Present and lies in the centre of the cell |
| Lysosomes | Present but are very rare | Present |
| Centrosomes | Absent | Present |
| Golgi Apparatus | Present | Present |
| Cytoplasm | Present | Present |
| Ribosomes | Present | Present |
| Plastids | Present | Absent |
| Vacuoles | Few large or a single, centrally positioned vacuole | Usually small and numerous |
| Cilia | Absent | Present in most of the animal cells |
| Mitochondria | Present but fewer in number | Present and are numerous |
| Mode of Nutrition | Primarily autotrophic | Heterotrophic |
Also refer :








