Difference Between Scandinavian And Nordic Countries:
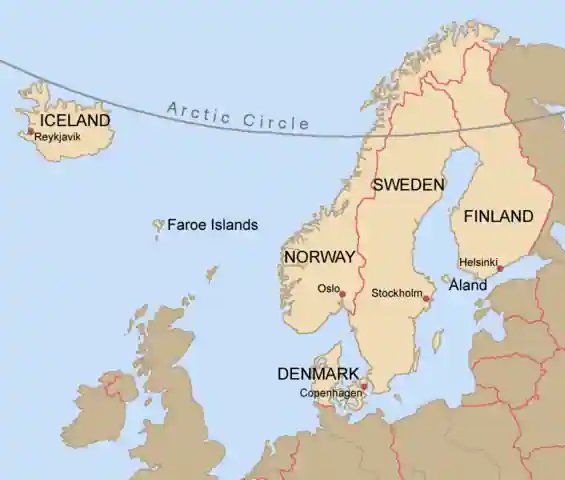
- Norway, Sweden and Denmark are called Scandinavian Countries.
- Scandinavia along with Finland and Iceland including Greenland and Faroe Islands are called Nordic Countries.
- Balkan Peninsula is comprised of Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Kosovo, Macedonia, Montenegro, Romania, Serbia, and Slovenia with portions of Greece and Turkey.
- Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania are called Baltic Countries.
- Greenland and Faroe Islands are autonomous constituent countries within the Kingdom of Denmark.
- The use of the word ‘Skandinavien’ is common in Swedish, Norwegian and Danish languages because that word refers to the ancient territories of the Norsemen: Norway, Sweden, and Denmark. Faroe Island and Iceland were the part of the Norsemen territory as well.
- Territories of the Norsemen is the most accepted way of recognising the Scandinavian countries.
- ‘Nordic’ is a term derived from the local Scandinavian-language word ‘Norden’ which in literal terms means, the northern islands. However, the residents are called as ‘Norbdo’ which in literal term means, “northern dwellers”.
- Nordic countries include Finland, Iceland, Norway, Denmark, Sweden, and the Faroe Islands (an archipelago of islands as an autonomous country within the kingdom of Denmark).
History
- The 8th to the 11th centuries are known as the Viking Age.
- Viking is not the name of a tribe or nation, but the Old Norse word for ‘sailor’. Most people from the territory of Norse were farmers who remained in Scandinavia and were by definition not Vikings, but some Norsemen.
- These Norsemen sailed through the stretch of Atlantic and the European rivers. They are also known to have taken part in the foundation of the nations like England, Russia and France.
- With due time, the Norsemen held a bad reputation across Europe. They were known for their barbarism as their expedition from peaceful trade turned into pirate raids.
- The Norse nations were unified by 1000 AD.
- Sweden annexed Finland in the 13th century. Sweden proving rebellious fought eleven wars against Denmark over a period of 300 years. The idea of Scandanavian unity was revived in the 19th century.
- Scandinavian history is properly known after the introduction of Christianity. In 829 AD, Denmark was the first of those countries to embrace Christianity.
- Erik, the heir of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, implemented a political unity of a period of 123 years that acknowledged Denmark as the political capital of Scandinavia.
- This union was broken with the establishment of independent Swedish monarch in a revolt led by Gustavus Vasa.
- Norway remained affiliated with Denmark and remained so until 1814 after the Swedish revolt. In this manner, the historical monarchies of Denmark and Norway were established on one side, and Sweden and Finland on the other.
- Finland was a colony of Russia since 1845 and got independence in 1918 due to weakened condition of Russia after World War 1.
- Norway’s independence in 1905 was set off from Denmark after 400 years of domination.
Also refer :








