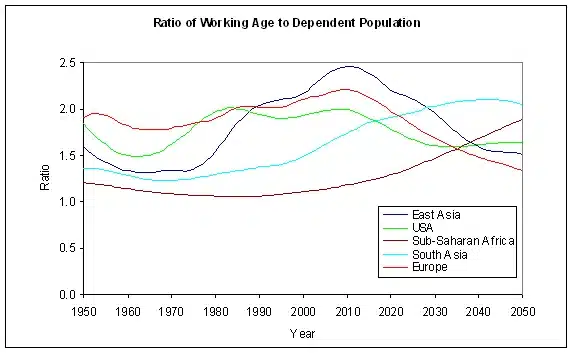
different financial sector regulators in India
In India, the financial sector is regulated with the help of independent regulators, associated with the field of insurance, banking, commodity market, and capital market and also the field of pension funds.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI): financial sector regulator
- The Reserve Bank of India is the apex monetary Institution of India.
- It is also called the Central Bank of India.
- The Reserve Bank of India was established on April 1, 1935 in accordance with the provisions of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- The Central Office of the Reserve Bank was initially established in Calcutta but was permanently moved to Mumbai in 1937.
- Though originally privately owned, since nationalization in 1949, the Reserve Bank of India is fully owned by the Government of India.
- RBI is the financial regulator of all the financial institutions like public sector banks, private sector banks, RRBs, Cooperative banks and all type of non-banking financial companies.
- The main function of RBI is to control the inflation of the country keeping in mind the growth of the country.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI): financial sector regulator

- SEBI also form a major part under the financial body of India.
- This is a regulator associated with the security markets in Indian Territory.
- Established in the year 1988, the SEBI Act came into power in the year 1992.
- Headquarter : Mumbai
Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI): financial sector regulator
- The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA) is a national agency of the Government of India.
- It was formed by an Act of Indian Parliament known as IRDA Act 1999, which was amended in 2002 to incorporate some emerging requirements.
- Headquarter : Hyderabad.
- It comprised of the Indian Parliamentary Act and was passed duly by the Indian government.
- Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India is the regulator of all private sector insurance business and public sector insurance business in India.
- IRDA issues guidelines for various insurance companies.
- It regulates the functioning of insurance companies to direct them to work in the public interest.
Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA): financial sector regulator
- Pension Fund regulatory is a pension related authority, which was established in the year 2003 by the Indian Government.
- Headquarter : New Delhi
- It is authorized by the Finance Ministry, and it helps in promoting income security of old age by regulating and also developing pension funds.
- This group can also help in protecting the interest rate of the subscribers, associated with the schemes of pension money along with the related matters.
- PFRDA is also responsible for the appointment of different other intermediate agencies like Pension Fund managers.
Forward Markets Commission: financial sector regulator
- It is the chief regulator of the commodity (MCX, UCX, NMCE etc) of the Indian future market
- It’s headquarter is located in Mumbai.
- Working in collaboration with the Finance Ministry.
- The main objective of this body is to advise the Central government on matters of the Forwards Contract Act, 1952.
Also, refer :
- Top 50 Science MCQs For Competitive Exams
- Know About The Different Financial Sector Regulators In India
- Monetary policy of RBI.