Ecotone, Edge Effect And Ecological Niche
Ecotone
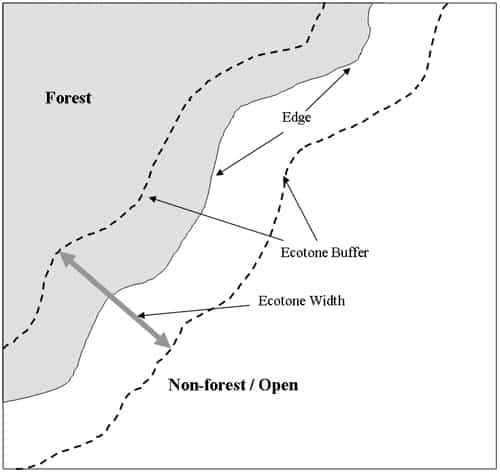
- An ecotone is a zone of junction or a transition area between two biomes (diverse ecosystems).
- Ecotone is the zone where two communities meet and integrate.
- For e.g. the mangrove forests represent an ecotone between marine and terrestrial ecosystem.
- Other examples are grassland (between forest and desert), estuary (between fresh water and salt water) and riverbank or marshland (between dry and wet).
Characteristics of Ecotone
- It may be narrow (between grassland and forest) or wide (between forest and desert).
- It has conditions intermediate to the adjacent ecosystems. Hence it is a zone of tension.
- Usually, the number and the population density of the species of an outgoing community decreases as we move away from the community or ecosystem.
- A well-developed ecotone contains some organisms which are entirely different from that of the adjoining communities.
Ecocline
- Ecocline is a zone of gradual but continuous change from one ecosystem to another when there is no sharp boundary between the two in terms of species composition.
- Ecocline occurs across the environmental gradient (gradual change in abiotic factors such as altitude, temperature (thermocline), salinity (halocline), depth, etc.).
Edge Effect – Edge Species
- Edge effect refers to the changes in population or community structures that occur at the boundary of two habitats (ecotone).
- Sometimes the number of species and the population density of some of the species in the ecotone is much greater than either community. This is called edge effect.
- The organisms which occur primarily or most abundantly in this zone are known as edge species.
- In the terrestrial ecosystems edge effect is especially applicable to birds.
- For example, the density of birds is greater in the ecotone between the forest and the desert.
Ecological Niche
- Niche refers to the unique functional role and position of a species in its habitat or ecosystem.
- The functional characteristics of a species in its habitat is referred to as “niche” in that common habitat.
- In nature, many species occupy the same habitat, but they perform different functions:
- habitat niche – where it lives, food niche – what is eats or decomposes & what species it competes with,
- reproductive niche – how and when it reproduces,
- physical & chemical niche – temperature, land shape, land slope, humidity & another requirement.
- Niche plays an important role in the conservation of organisms. If we have to conserve species in its native habitat, we should have knowledge about the niche requirements of the species.
Difference between niche and habitat
- The habitat of a species is like its ‘address’ (i.e. where it lives) whereas niche can be thought of as its “profession” (i.e. activities and responses specific to the species). For example, various habitats of house sparrow include woodlands, grasslands, and deserts; houses, factories, warehouses, zoos etc. However when we talk about its niche, it would include – eating insects, grains, seeds etc.; making nests in houses, trees and shrubs etc. Thus, niche is a broader concept than habitat and its focus is on functional role played by the species rather than only the place it needs to live. For any organism, the niche includes both the physical habitat and how it has adopted to life in that habitat.
- A niche is unique for a species while many species share the habitat.
- No two species in a habitat can have the same niche. This is because of the competition with one another until one is displaced.
- For example, a large number of different species of insects may be pests of the same plant, but they can co-exist as they feed on different parts of the same plant.
Ecological Equivalents
- Organisms that occupy the same or similar ecological niches in different geographical regions are known as Ecological Equivalents.
- For examples, owls and cats, both feed on mice; but owls are found in deserts or forests while cats are around human habitations.
- In this context, owls and cats are ecological equivalents in terms of their feeding role.
- Similarly, Kangaroos of Australia perform the same functions (herbivores) as antelopes or Bison of North America. Both live in similar habitats of different regions but have similar profession of herbivores.
Also refer :








