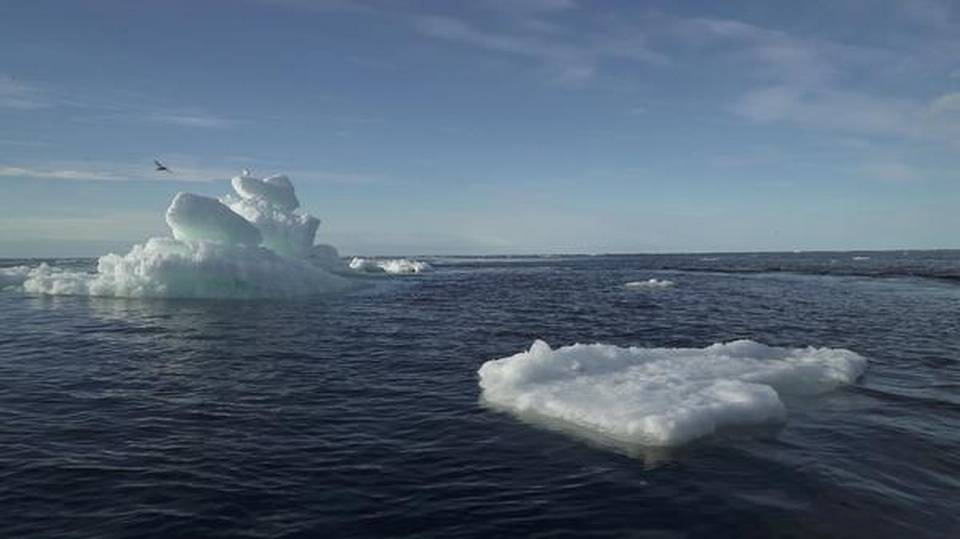
Due To Ice Loss Global Temperature Is Likely To Increase
Scientists at Germany’s Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) found that under current levels of atmospheric CO2 — roughly 400 parts per million — the melting of Arctic sea ice, mountain glaciers and the polar ice caps would raise temperatures by 0.4 degree celsius.
Reason
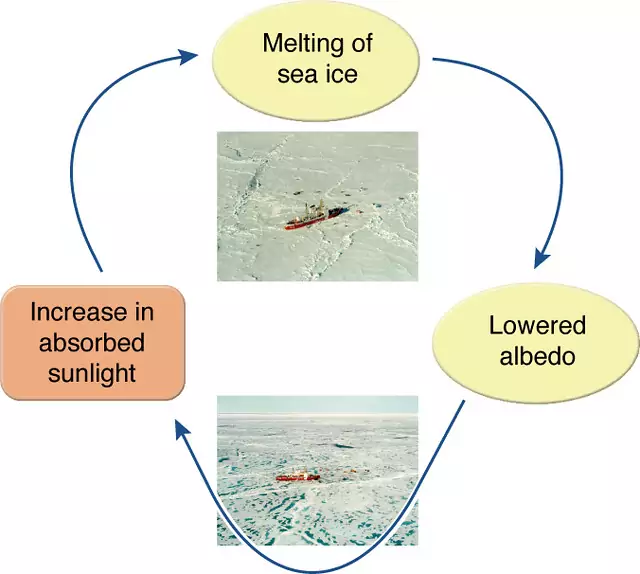
The main driver of temperature gain from ice loss would be due to a process known as albedo effect.
What is Albedo Effect?
Albedo is the measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0 to 1.
- 0 means black body that absorbs all incident radiation.
- 1 means a body that reflects all incident radiation.
Ice cap has very high albedo means it reflects very high amount of incident radiation. But when ice caps, glaciers etc are melted then less amount of incident radiation are reflected and more amount are absorbed which increases the temperature and due to which more ice are melted .
This is called “feedback loop” in which increased temperatures lead to further ice loss, which in turn further increases temperatures.
Other ways that temperatures would rise further as ice receded include increased water vapour in the atmosphere, increasing the greenhouse effects.
Tipping Point
The ice lost in a given year would be replenished by wintertime snowfall, and the sheet maintained a near-constant mass.
With continued global warming, it becomes more and more likely that we cross tipping points — not just in the ice-sheets, but also in other parts of the climate system i.e. irreversible change in the climate system.
Also refer :