इस आर्टिकल को हिंदी में पढने के लिए यहाँ क्लिक करें.
General Information about Bihar
| State Formation Day | 22 March 1912 |
|---|---|
| First Division of Bihar | 1936 (Odisha) |
| Second Division of Bihar | 15 November 2000 (Jharkhand) |
| Governor | Shri Arif Mohammad Khan |
| Chief Minister | Shri Nitish Kumar (9th time) |
| Deputy Chief Minister | Shri Samrat Chaudhary, Shri Vijay Kumar Sinha |
| Legislature | Bicameral Legislative Council 75 Legislative Assembly 243 |
| Lok Sabha Seat | 40 |
| Rajya Sabha Seat | 16 |
| High Court | Patna High Court |
| Chief Justice | Justice Vipul M. Pancholi (45th) |
| Area | 94,163 km2 |
| Population (2011) | 10,40,99,452 |
| Density | 1,106/km2 |
| Official language | Hindi |
| Maximum Spoken Regional Language | Maithili |
| Divisions | 9 |
| Districts | 38 |
| Sub-Divisions | 101 |
| CD Blocks | 534 |
Bihar Map: Information About Bihar
Bihar is located in the eastern part of the country (between 83°-19′-50″ to 88°-17′-40″ E longitude). It is an entirely landlocked state, although the outlet to the sea through the port of Kolkata is not too far away. Bihar lies mid-way between the humid West Bengal in the east and the sub-humid Uttar Pradesh in the west, providing it with a transitional position regarding climate, economy and culture. It is bounded by Nepal in the north and by Jharkhand in the south. The Bihar plain is divided into two unequal halves by the river Ganga which flows through the middle from west to east.
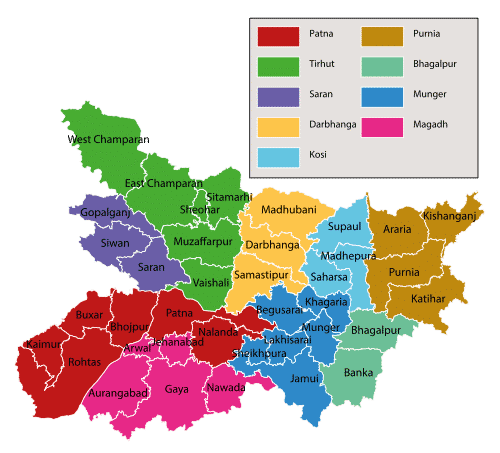
- 7 Districts border Nepal in the west-to-east direction: West Champaran, East Champaran, Sitamarhi, Madhubani, Supaul, Araria and Kishanganj
- 8 Districts that border Uttar Pradesh in the north to south direction: West Champaran, Gopalganj, Siwan, Saran, Bhojpur, Buxar, Kaimur and Rohtas
- 8 Districts that border Jharkhand in the west to east direction: Rohtas, Aurangabad, Gaya, Nawada, Jamui, Banka, Bhagalpur and Katihar
- 3 Districts that border West Bengal in the north-to-south direction: Kishanganj, Purnia and Katihar
बिहार आर्थिक सर्वेक्षण : 2024-25
Physical Features: Information About Bihar
| Latitude | 24°-20′-10″ ~ 27°-31′-15″ N |
|---|---|
| Longitude | 83°-19′-50″ ~ 88°-17′-40″ E |
| Total Area | 94,163.00 sq. kms |
| Height above Sea-Level | 173 Feet |
| Distance from east to west | 483 km |
| Distance from north to south | 345 km |
| Length of Nepal border | 601 km |
2011 Census: Information About Bihar
| Density of Population | 1,106 per sq kms |
|---|---|
| Highest Density | Sheohar, 1880 per sq kms |
| Lowest Density | Kaimur, 488 per sq kms |
| Most Populous District | Patna: 58,38,465 |
| Least Populous District | Sheikhpura: 6,36,342 |
| Sex Ratio (Females/Thousand Males) | 918 |
| Highest Ratio | (Gopalganj) 1,021 |
| Lowest Ratio | (Munger) 876 |
| Lowest Literacy Rate | Purnia, 51.08% |
| Highest Literacy Rate | Rohtas, 73.37% |
Symbols: Information About Bihar
| State Animal | Gaur |
| State Bird | House Sparrow |
| State Flower | Marigold |
| State Tree | Peepal |
First in Bihar: Information About Bihar
- Sugar Mill : Madhaura (1904)
- Nagarpalika : Ara (1865)
- Irrigation Project : Son Multipurpose Project
- Lok Sabha Speaker : Baliram Bhagat
- English Newspaper Daily : The Search Light
- English Newspaper Weekly : The Bihar Herald
- Hindi Newspaper Weekly : Bihar Bandhu
- Hindi Newspaper Daily : Sarvhitaishi
- Neolithic age ornaments : Chirand
- Chief Minister : Sri Krishna Singh
- Governor : Jai Ram Das Daulat Ram
- T.V. relay centre : Muzaffarpur (1978)
- Oil Refinery Centre : Barauni
Geological Structure: Information About Bihar
- Younger rocks to the north, older rocks to the south
- North-West is Terai, Central is Gangetic plain and South is a plateau
- Bihar plain is the youngest to be formed
- Dharwar rocks – South eastern Bihar – Jamui, Nawada, Munger districts
- Vindhyan Rocks – South Western Bihar – Kaimur, Rohtas districts
Waterfalls: Information About Bihar
- Kakolat Falls (Nawada)
- Telhar Waterfall (Kaimur)
- Karkat Waterfall (Kaimur)
- Tutla Bhawani(Tutrahi or Titula Dham) (Rohtas)
- Dhua kund Waterfall (Rohtas)
Springs in Bihar: Information About Bihar
- Manjhar Kund (Rohtas)
- Dhua Kund (Rohtas)
- Sita Kund (Sitamarhi)
- Hot Spring (Rajgir )
Lakes: Information About Bihar
- Kanwar Lake (Begusarai)
- Muchalinda Lake (Bodhgaya)
- Saraiya Man Lake (Bettiah)
- Kharagpur Lake (Munger)
- Moti Jheel (Motihari)
- Pandu Pokhar (Rajgir)
- Ghorakatora Lake (Rajgir)
World Heritage Sites: Information About Bihar
- Archaeological Site of Nalanda Mahavihara (Nalanda University): Nalanda (2016)
- Mahabodhi Temple Complex : Bodh Gaya (2002)
Ramsar Sites: Information About Bihar
- Kanwar Lake: Begusarai
- Nagi Bird Sanctuary (81st): Jamui
- Nakti Bird Sanctuary (82nd): Jamui
The surname of Important Personalities: Information About Bihar
| Name | Surname |
| Dr. Rajendra Prasad | Deshratna, Ajatshatru |
| Jai Prakash Narayan | Loknayak, JP |
| Kunwar Singh | Babu |
| Dr. Shri Krishna Singh | Bihar Kesari |
| Ramdhari Singh Dinkar | Rashtra Kavi |
| Babu Jagjivan Ram | Babujee |
| Baidya Nath Misra | Baba, Nagarjun |
| Dr. Anugraha Narayan Sinha | Bihar Bibhuti |
| Vidyapati | Bihar Kokil |
Protected Areas: Information About Bihar
बिहार के राष्ट्रीय उद्यान और वन्यजीव अभयारण्य
| SL | Name of Park/Sanctuary | District |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Barela SAZS Sanctuary | Vaishali |
| 2. | Bhimbandh Sanctuary | Monghyr |
| 3. | Gogabil Pakshi Vihar | Katihar |
| 4. | Gautambuddha Sanctuary | Gaya |
| 5. | Kaimur Sanctuary | Rohtas |
| 6. | Kanwar Jheel Bird Sanctuary | Begusarai |
| 7. | Kusheshwarsthan | Darbhanga |
| 8. | Nagi Dam Bird Sanctuary | Jamui |
| 9. | Nakti Dam Bird Sanctuary | Jamui |
| 10. | Rajgir Sanctuary | Nalanda |
| 11. | Sanjay Gandhi Botanical Garden | Patna |
| 12. | Udaypur Sanctuary | West Champaran |
| 13. | Valmiki National Park | West Champaran |
| 14. | Valmiki Sanctuary | West Champaran |
| 15. | Vikramshila Gangetic Dolphin | Bhagalpur |
GI Tags: Information About Bihar
| Mithila Makhana |
| Silao Khaja |
| Muzaffarpur’s Shahi Litchi |
| Katarni Dhaan (rice) |
| Nawada’s Magahi Paan |
| Bhagalpur’s Jardalu Mango |
| Manjusha Art |
| Bhagalpur Silk |
| Madhubani Paintings |
| Sujini Embroidery work |
| Sikki Grass Product |
| Applique (Khatwa) Work |
| Stone Art of Gaya |
Miscellaneous Facts: Information About Bihar
- Pre-Stone and Mesolithic tools have been found in Munger and Nalanda.
- Materials of the Neolithic Age have been found in Chirand (Saran) and Chechar (Vaishali).
- In Rigveda, the words ‘Keekat’ and ‘Bratya’ have been used for the Bihar region.
- The Shatapatha Brahmana describes the arrival and settlement of Aryans in Bihar.
- According to Vayu Purana, Gaya was ruled by Asuras.
- The Mahajanapadas located in the ancient vihara were: Anga, Magadha and Vajji.
- Anga and Magadh are mentioned in the Atharvaveda.
- Chandragupta II made Ujjain the capital of Magadha in place of Pataliputra.
- The most popular Sufi silsila in Bihar was Firdausi.
- Mulla Bahbahani salt traveler called Patna the heaven of India.
- Farrukhshiyar was the first Mughal emperor whose coronation took place in Patna (Bihar) in 1713 AD.
- Nalanda Mahavihara was built during the reign of Kumar Gupta I.
- Mulla Bahbahani, a salt traveler called Patna the heaven of India.
- Prince Azim had named Patna as Azimabad.
- Udayin shifted his capital from Rajagriha and established it at Pataliputra.
- Shishunaga made Vaishali his second capital apart from Giribraj. Later Vaishali became his principal capital.
- Nanyadev was the founder of the Karnat dynasty.
- Devpal made Munger his capital.
- During the time of Tughlaq, the capital was at Biharsharif in the present Nalanda district.
- Akbar’s governor Raja Man Singh made Rohtas his capital.
- Captain John Garstin built the Golghar in 1786 AD.
- Farrukh Siyar was the first Mughal emperor who was coronated in Bihar.
- The coronation of Shah Alam II in Bihar took place under the protection of the British.
- Sachindranath Sanyal had established a branch of Anushilan Samiti in Patna in 1913.
- Revati Nag was sent by Dhaka Anushilan Samiti to Bhagalpur to campaign for revolution.
- In 1918, ‘Bihari Yuvak Sangh’ was established in Motihari.
- In 1927 AD, ‘Patna Yuvak Sangh’ was established.
- In 1929 AD, ‘Pataliputra Youth Association’ was established.
- The Bihar Socialist Party was formed by Jayaprakash Narayan and Phoolan Prasad Verma in 1931.
- The Indian Congress Socialist Party was established in Patna in 1934 AD.
Also, refer to the following:
- Download BPSC 66th prelims question paper: हिंदी में, English.
- महिला सशक्तिकरण के लिए बिहार सरकार की महत्वपूर्ण योजनाएँ
- बिहार के लोक-नृत्य
- Download the pdf of Important MCQs From the History Of Ancient India
- List Of Important Inscriptions In India