Definition of Clouds
Cloud is a mass of minute water droplets or tiny crystals of ice formed by the condensation of the water vapour in free air at considerable elevations.
- Clouds are formed due to condensation of water vapour around hygroscopic nuclei caused by cooling due to lifting of air generally known as adiabatic cooling.
- It may be mentioned that not all clouds yield precipitation but no precipitation is possible without cloud.
- Clouds play major role in the heat budget of the earth and the atmosphere as they reflect, absorb and diffuse some part of incoming shortwave solar radiation and absorb some part of outgoing longwave terrestrial radiation and then re- radiate it back to the earth’s surface.
What are the different types of clouds?
Clouds are classified primarily based on – their shape and their altitude.
Based on shape, clouds are classified into three. They are:
- Cirrus
- Cumulus
- Stratus
Based on the height or altitude the clouds are classified into three. They are –
- High Clouds
- Middle Clouds
- Low Clouds
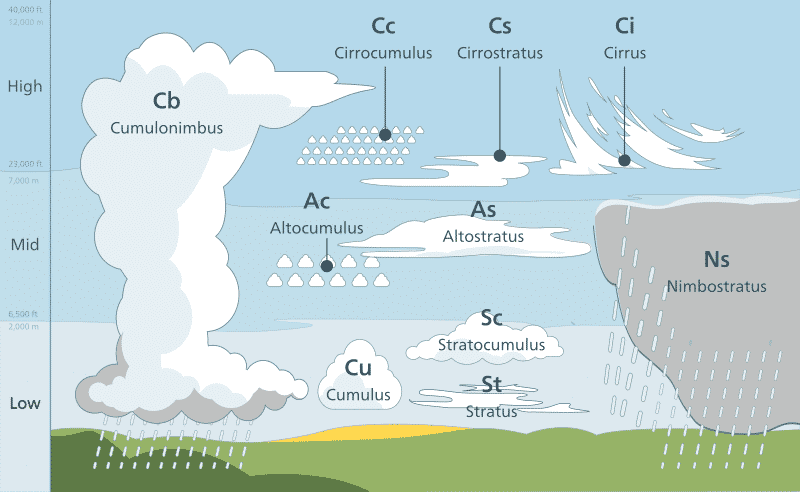
1) High Clouds
- They can reach above 6000 metres or 20,000 feet.
- They are also known as Cirrus Clouds.
- They are usually thin and are made up of ice.
- They often indicate fair weather and hence do not produce rain.
| Types of High Clouds | Description |
| 1. Cirrus | |
| 2. Cirrostratus | |
| 3. Cirrocumulus |
2) Middle Clouds
- They form between 6,500 feet and cirrus level or from 2000 to 6000 metres.
- They are also known as “Alto” clouds.
- They frequently indicate an approaching storm.
- They may sometimes produce Virga, which is a rain or snow that does not reach the ground.
| Types of Middle Clouds | Description |
| 1. Altostratus | These clouds are in the form of continuous sheet or veil, grey or blue-gray in colour. They are composed of ice crystals and water droplets. In its thinner areas, the sun can still be visible as a round, dim disk. These clouds may often form ahead of storms with continuous rain or snow. |
| 2. Altocumulus | They are greyish sheet cloud, characterised by globular masses or rolls in layers or patches, the individual elements being larger and darker than those of cirrocumulus and smaller than those of stratocumulus. |
3) Low Clouds
- They lie below 6,500 feet, which means from the surface to 2,000 meters.
- Low clouds are also known as Stratus Clouds.
- They may appear dense, dark, and rainy (or snowy) and can also be cottony white clumps interspersed with blue sky.
| Types of Low Clouds | Description |
| 1. Strato Cumulus | Usually arranged in a large dark, rounded or globular masses, usually in groups, lines, or waves. |
| 2. Stratus | Usually looks like a huge grey blanket that hangs low in the sky that resembles fog, comprises uniform layer and appear dull, if these clouds are warm it means rain and if it is cold it snows. |
| 3. Nimbostratus | They are known as ‘Rain Clouds’ and they are dark, thick and accompanied by light to moderately falling precipitation. |
Clouds with vertical development
- They form between 490 m to 10,600 m.
- Cumulus (meaning pile or heap) is vertically thick cloud with a dome shaped cauliflower top and a horizontal base. These clouds are evidence of strong vertical convection currents and they bring rain.
- Cumulo-nimbus are overgrown cumulus clouds which have reached such a height that they lose their cauliflower shape. They often spread out on top of anvil. Such clouds are associated with sharp showers, squally winds lightening, thunder and sometimes hail.
Why clouds appear white in colour?
- The clouds usually appear white because the tiny water droplets and ice crystals inside them are tightly packed, and they reflect most of the sunlight that falls on these masses (scattering).
- The tiny cloud particles equally scatter all colours of light, which make the viewer to perceive all wavelengths of sunlight mixed together as white light.
Why do clouds darken at the time of rain?
- The clouds appear dark or grey in colour at the time of rain is due to their particulate density.
- The water vapour will bind together into raindrops, leaving larger spaces between these drops of water and hence less amount of light is reflected, lending a darker appearance of the rain clouds.
Also refer :