Know About Lakes
Lake is a surface water body that is surrounded by land. Rivers will be outlet or inlet to the lakes i.e. lakes take the water from rivers or act as a source of water.
- A lake (from Latin lacus) is a large body of water (larger and deeper than a pond) within a body of land.
- As a lake is separated from the ocean, it is not a sea.
- Some lakes are very big, and people in the past sometimes called them seas.
- Lakes do not flow like rivers, but many have rivers flowing into and out of them.
- Most lakes on the surface of the Earth are fresh water and most are in the Northern Hemisphere.
- More than 60% of the lakes of the world are in Canada.
- Finland is known as The Land of the Thousand Lakes (there are 187,888 lakes in Finland, of which 60,000 are large).
Largest lakes by continent
- Africa – Lake Victoria, also the second largest freshwater lake on Earth. It is one of the Great Lakes of Africa.
- Antarctica – Lake Vostok.
- Asia – Lake Baikal is the largest lake that is completely in Asia. The Caspian Sea, the largest lake on Earth, is on the Europe-Asia border (an artificial border) and so both continents share this lake.
- Australia – Lake Eyre, that most of the time is without water; it takes water when it rains a lot.
- Europe – Lake Ladoga, followed by Lake Onega, both in northwestern Russia.
- North America – Lake Superior.
- South America – Lake Maracaibo but it is like a bay because it has a wide opening to sea. The largest freshwater lake of South America is Lake Titicaca, which is also the highest body of water on Earth at 3,821 m (12,507 ft) above sea level where boats can travel.
Important Facts on lakes of the world
- The largest lake in the world by area is the Caspian Sea, with 394,299 km².
- The largest freshwater lake by area is Lake Superior (82,414 km²), part of the Great Lakes.
- Lake Michigan is the largest lake (by area) that is located entirely in one country.
- The longest freshwater lake is Lake Tanganyika, with a length of about 660 km. Lake Baikal is the second longest (about 630 km from tip to tip).
- The deepest lake is Lake Baikal in Siberia, with a bottom at 1,637 m (5,371 ft). Lake Tanganyika (1,470 m) is the second deepest lake.
- The highest lake of the world is a small lake (pond) without a name on Ojos del Salado at 6,390 m (20,965 ft). But the highest navigable lake is Lake Titicaca in Peru and Bolivia at 3,812 m (12,507 ft).
- The lowest lake of the world is the Dead Sea, bordering Israel and Jordan at 418 m (1,371 ft) below sea level. It is also one of the lakes with highest salt concentration.
- Lake Enriquillo in Dominican Republic is the only saltwater lake in the world where crocodiles live.
- Lake Huron Contains Manitoulin Island, the world’s largest lake island.
- The much larger Lake Maracaibo is a contiguous body of water with the sea, so it is ignored.
- Black Sea is not a lake since Bosporus and Dardanelles Straits connect it to the Mediterranean Sea. Many big rivers fall into the Black Sea, making the salinity of its surface water half that of the ocean: 17‰.
- Caspian Sea and the Dead Sea are lakes. The surface and shores of the Dead Sea are 423 meters below sea level, making it Earth’s lowest elevation on land.
| Largest lake of Asia | Caspian Sea |
| Largest lake of Europe | Lake Ladoga |
| Largest lake of North America | Lake Superior |
| Largest lake of South America | Lake Titicaca |
| Largest lake of Africa | Lake Victoria |
| Largest lake of Oceania | Lake Eyre |
| Largest salt water lake of the world | Caspian Sea |
| Largest fresh water lake of the world by surface area | Lake Superior |
| Largest fresh water lake of the world by volume | Lake Baikal |
| World’s deepest lake | Lake Baikal |
| Longest freshwater lake in the world | Lake Tanganyika |
| Highest navigable lake in the world | Lake Titicaca |
Caspian Sea
- The Caspian Sea (also known as Mazandaran Sea, Hyrcanian Ocean, or Khazar Sea) is the world’s largest inland body of water, often described as the world’s largest lake or a full-fledged sea.
- An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau of Western Asia.
- Border countries : Kazakhstan, Iran, Azerbaijan, Russia, Turkmenistan.
| Max. length | 1,030 km (640 mi) |
|---|---|
| Max. width | 435 km (270 mi) |
| Surface area | 371,000 km2 (143,200 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 211 m (690 ft) |
| Max. depth | 1,025 m (3,360 ft) |
| Water volume | 78,200 km3 (18,800 cu mi) |
Lake Baikal – Deepest Lake
- Lake Baikal is a rift lake located in southern Siberia, Russia.
- It is the largest freshwater lake by volume in the world, containing 22 to 23% of the world’s fresh surface water.
- It is the seventh-largest lake in the world by surface area.
- Maximum depth: 1,642 m (5,387 ft)
- It is the world’s oldest (25–30 million years) and deepest lake.
- It has a long, crescent shape.
- UNESCO declared Lake Baikal a World Heritage Site in 1996.
Lake Tanganyika – Longest Lake
- The longest lake in the world. [660 kilometres long]
- It is also the second largest by volume.
- It is the second deepest lake in the world, after lake Baikal.
Great Lakes
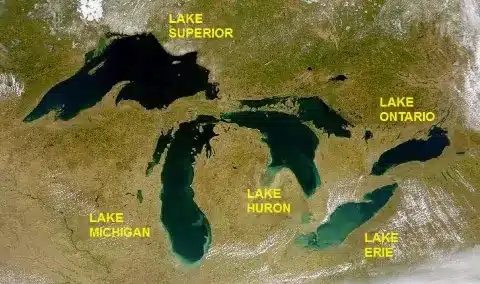
- Great Lakes of North America are a series of interconnected freshwater lakes which connect to the Atlantic Ocean through the Saint Lawrence Seaway.
- Consisting of Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario [in the order of west to east].
- Superior, Huron, Michigan, Erie, and Ontario [In the order of largest to smallest].
- Lake Superior is the largest continental lake in the world by area, and Lake Michigan is the largest lake that is entirely within one country
- The Great Lakes are today used as a major water transport corridor for bulk goods.
- The Great Lakes Waterway connects all the lakes; the smaller Saint Lawrence Seaway connects the lakes to the Atlantic oceans.
Dead Sea
- Also called the Salt Sea.
- Lake bordering Jordan to the east, and Palestine and Israel to the west.
- It Earth’s lowest elevation on land.
Aral Sea
- It was a lake lying between Kazakhstan in the north and Uzbekistan, in the south.
- Aral Sea has been steadily shrinking since the 1960s after the rivers that fed it were diverted by Soviet irrigation projects.
African Great Lakes
- Series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift.
- They include Lake Victoria, the second-largest freshwater lake in the world, and Lake Tanganyika, the world’s second-largest in volume as well as the second deepest.
Also refer :