Unemployment in India
Definition of Unemployment
Unemployment is a situation in which individuals are ready and willing to work at the prevailing rate of wages but the individuals could not get work.
According to NSSO, a person will be in one or a combination of the following three statuses during a reference period.
- Working or being engaged in economic activity (work)
- Being not engaged in economic activity (work) and either making tangible efforts to seek ‘work’ or being available for ‘work’ if the work is available and
- Being not engaged in any economic activity (work) and also not available for ‘work’.
Persons in categories (1) and (2) above are called labour force.
Persons in the categories (1) are called employed. They also termed as work force.
Persons in the category (2) are called unemployed.
Persons in the category (3) are termed as not in the labour force.
Number of unemployed = Labour force – Work force.
Types of Unemployment in India
- Cyclical Unemployment:
- It is caused due to business cycle. This kind of an unemployment occurs when all those who want to work cannot be employed because there is not enough demand in the market for their work. It is called as, cyclical unemployment because it varies with the trade cycle.
- Frictional Unemployment:
- This kind of unemployment occurs when a person leaves/loses a job and starts looking for another one. This search for a job may take a considerable amount of time resulting in frictional unemployment. Frictional unemployment tends to be on a high when an economy is not doing so well and low otherwise because during good times it will be easier for people to find jobs that match their skills and requirements easily.
- Seasonal Unemployment:
- This kind of unemployment is expected to occur at certain parts of the year. For example, the jobs at a hill station may experiences seasonal unemployment during the winter months because less people will visit these areas during this time.
- Structural Unemployment:
- This kind of unemployment happens when the structure of an industry changes. For example, as the country is tending to move from use of bicycles to motorbikes and cars, the demand for labor in the cycle industry has continuously fallen in the country.
- Full Employment:
- Employment would be full literally when every able-bodied adult works the number of hours considered normal for a fully employed person.
- Under Employment:
- This term can be used in multiple connotations but one of the primary usage is to showcase a situation where a person with high skills works in low wage and low skills job.
- Disguised Unemployment:
- Such type of unemployment is quite common in the agri-cultural sector in India. It occurs when people are employed in a job where their presence or absence does not make any difference to the output of the economy.
Causes of Unemployment in India
The major causes of unemployment in India are as mentioned below:
- Large population.
- Lack of vocational skills or low educational levels of the working population.
- The low productivity in the agriculture sector plus the lack of alternative opportunities for agricultural workers that makes transition among the three sectors difficult.
- Legal complexities, Inadequate state support, low infrastructural, financial and market linkages to small businesses making such enterprises unviable with cost and compliance overruns.
- Inadequate growth of infrastructure and low investments in the manufacturing sector, hence restricting the employment potential of the secondary sector.
- The huge workforce of the country is associated with the informal sector because of a lack of required education or skills, and this data is not captured in employment statistics.
- The main cause of structural unemployment is the education provided in schools and colleges are not as per the current requirements of the industries.
- Regressive social norms that deter women from taking/continuing employment.
- Fall of Cottage and Small industries: The industrial development had adverse effect on cottage and small industries. The production of cottage industries began to fall and many artisans became unemployed.
Impact Of Unemployment in India
The unemployment in any nation have the following effects on the economy:
- The problem of unemployment gives rise to the problem of poverty.
- The government suffers extra borrowing burden because unemployment causes a decrease in the production and less consumption of goods and services by the people.
- Unemployed persons can easily be enticed by antisocial elements. This makes them lose faith in the democratic values of the country.
- People unemployed for a long time may indulge in illegal and wrong activities for earning money which increases crime in the country.
- Unemployment affects the economy of the country as the workforce that could have been gainfully employed to generate resources actually gets dependent on the remaining working population, thus escalating socio-economic costs for the state. For instance, a 1 % increase in unemployment reduces the GDP by 2 %.
- It is often seen that unemployed people end up getting addicted to drugs and alcohol or attempts suicide, leading to losses to the human resources of the country.
Phillips Curve
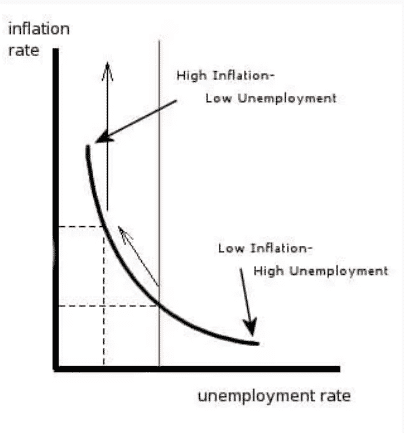
It is a graphic curve which advocates a relationship between inflation and unemployment in an economy. As per the curve there is a ‘trade of’ between inflation and unemployment, i.e., an inverse relationship between them. The curve suggests that lower the inflation, higher the unemployment and higher the inflation, lower the unemployment.
Nature of Unemployment in India:
India being a developing country, the nature of unemployment therefore is in stark contrast to the one observed in the developed countries. In developed countries, unemployment is driven by a fall in demand because as the demand for goods and services, machines fall idle and the demand for labour goes down.
But in India, the bigger problem is that of under-employment or disguised unemployment, which is not due to the lack of demand for goods but due to the shortage of capital equipment etc. in the economy. Because of lack of capital stock, India has not been able to commensurately meet the needs of the growing labour force in the country.
This manifests itself in two ways:
- The prevalence of large scale unemployment in the urban areas.
- In rural areas the growing numbers engaging themselves in the agricultural sector resulting in disguised unemployment.
As per one of NSS data 8.5 million people in the rural areas and 1.2 million people in the urban areas work for less than 14 hours a week resulting in underemployment.
What type of unemployment is found in Indian agricultural sector?
Disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment are two most common types of unemployments found in rural India particularly in farm sector.
What is the current unemployment rate in India?
As per Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE) data, the unemployment rate declined to 6.52 per cent in March 2021 from 9.1 per cent in December 2020.
Way Forwards
The basic solution to the entire problem is a faster rate of capital formation so as to enlarge employment opportunities. For this the government needs to encourage savings and their productive utilization in increasing the rate of investment. The state itself can participate in the process of capital formation by undertaking such development activities as the private entrepreneurs do not find it profitable to undertake. There is also a need for the government to increase and attract more foreign investment in a country like India.
Unemployment in India – Important Questions
Q1. Unemployment that occurs during the normal workings of an economy as people change jobs and move across the country is called _____.
- structural unemployment.
- natural unemployment
- frictional unemployment
- cyclical unemployment
Answer (3) Frictional unemployment
Q2. The natural rate of unemployment is generally thought of as the
- the sum of frictional unemployment and structural unemployment
- the ratio of the frictional unemployment rate to the cyclical unemployment rate
- the sum of frictional unemployment and cyclical unemployment
- the sum of structural unemployment and cyclical unemployment
Answer (1) the sum of frictional unemployment and structural unemployment
Q3. A sales manager of an equipment manufacturing company loses his job because the company relocated the unit to another country is an example of ____ unemployment.
- Seasonal unemployment
- Frictional unemployment
- Cyclical unemployment
- Structural unemployment
Answer (4) Structural unemployment
Q4. When the rate of unemployment increases because of recession or depression. It is which type of unemployment?
- Structural unemployment
- Seasonal unemployment
- Cyclical Unemployment
- Frictional Unemployment
Answer (3) Cyclical Unemployment
Q5. Discouraged workers are not considered as a part of the labour force, so classifying them as unemployed would
- have an indeterminate impact on the unemployment rate
- not change the unemployment rate
- increase the unemployment rate
- decrease the unemployment rate
Answer (3) increase the unemployment rate
You may be interested in the following topics